문제 먼저 읽기
- Trie 를 구현하세요
- Trie() trie를 초기화합니다.
- void insert(String word) 를 insert 합니다.
- boolean search(String word) word가 있으면 true, 없으면 false를 반환합니다.
- boolean startsWith(String prefix) 이미 존재하는 단어중에 prefix로 시작하는 단어가 있으면 true, 아니면 false를 반환합니다.
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
어떻게 풀까?
생각
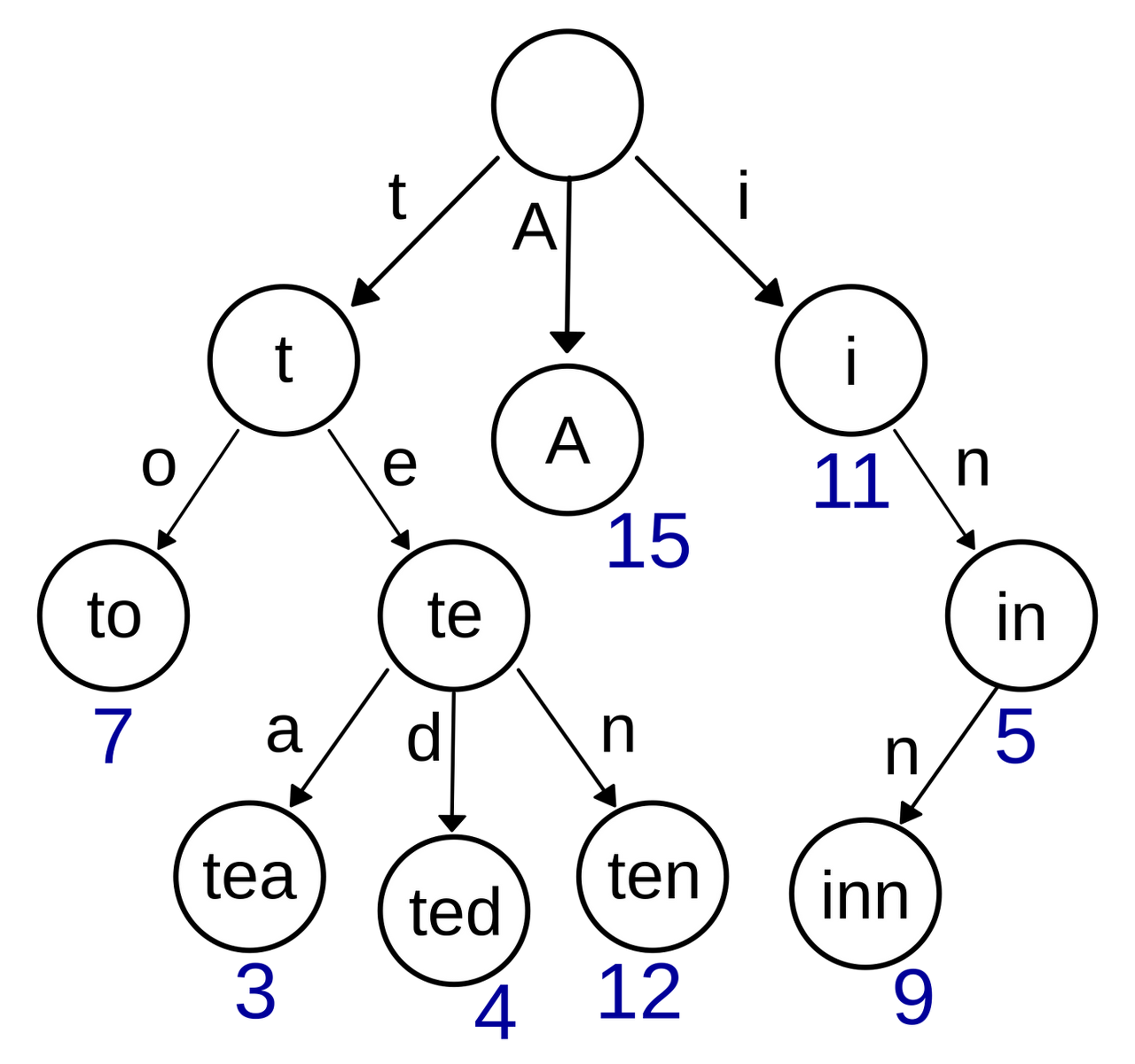
Trie 자료구조는 무엇인가?
- Trie : 문자열을 저장하고 효율적으로 탐색하는 트리 형태 자료구조입니다.
- 루트에서부터 리프를 향해 가면서 거치는 문자들을 합쳐 저장된 단어를 검색할 수 있습니다.
- 노드의 모든 자식 노드들은 해당 부모 노드와 연결된 문자열을 공통 접두사로 가집니다.

이미지 출처 : wiki
- 자동완성, 사전 검색 등에 사용할 수 있습니다.
수도코드
- 최근 Trie에 대해 수업을 들었던터라 기본 구현은 어렵지 않았습니다.
class Trie {
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
insert(this.root, word); // 재귀로 구현
}
public void insert(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0) { // 단어가 다 끝나면 끝
node.isEndOfWord = true;
return;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
node.children.put(c, child);
insert(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(this.root, word); // 똑같이 재귀로 구현
}
public boolean search(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0) { // 단어 끝과 tie 끝이 동일해야 한다.
return node.isEndOfWord;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
if (child==null) return false;
return search(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(this.root, prefix);
}
public boolean searchPrefix(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0 ) {
return true;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
if (child==null) return false;
return searchPrefix(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
}
class Node {
Map<Character, Node> children;
boolean isEndOfWord; // 초기화되면 바로 true가됩니다.
public Node() {
this.children = new HashMap<>();
this.isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
- 위 코드에서 child가 null인 경우 처리를 제대로 못해줘서 오류가 많이 나
class Trie {
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
insert(this.root, word);
}
public void insert(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0) { // 단어가 다 끝나면 끝
node.isEndOfWord = true;
return;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
**if (child == null) {
child = new Node(); // 이 부분이 문제였다.
node.children.put(c, child);
}**
insert(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(this.root, word); // 똑같이 재귀로 구현
}
public boolean search(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0) { // 단어 끝과 tie 끝이 동일해야 한다.
return node.isEndOfWord;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
if (child==null) return false;
return search(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(this.root, prefix);
}
public boolean searchPrefix(Node node, String word) {
if (word.length() == 0 ) {
return true;
}
char c = word.charAt(0);
Node child = node.children.get(c);
if (child==null) return false;
return searchPrefix(child, word.substring(1)); // 재귀
}
}
class Node {
Map<Character, Node> children;
boolean isEndOfWord; // 초기화되면 바로 true가됩니다.
public Node() {
this.children = new HashMap<>();
this.isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
결과
<aside> 💡 Success
Runtime: 44 ms, faster than 27.70% of Java online submissions for Implement Trie (Prefix Tree).
Memory Usage: 54.8 MB, less than 45.55% of Java online submissions for Implement Trie (Prefix Tree).
</aside>
다른 풀이 방식과 문제 회고
- sample 30 ms submission
- 알파벳이라는 특성을 살려 Map이 아니라 배열로 구현하면 훨씬 빠른 속도로 처리가 됩니다.
- 알파벳일 경우는 늘 경우의 수가 한정되기 때문에 배열을 최우선으로 고려해봐야겠습니다.
class Trie {
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
root.insert(word, 0);
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return root.search(word, 0);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return root.startsWith(prefix, 0);
}
class Node {
Node[] nodes;
boolean isEnd;
Node() {
nodes = new Node[26];
}
private void insert(String word, int idx) {
if (idx >= word.length()) return;
int i = word.charAt(idx) - 'a';
if (nodes[i] == null) {
nodes[i] = new Node();
}
if (idx == word.length()-1) nodes[i].isEnd = true;
nodes[i].insert(word, idx+1);
}
private boolean search(String word, int idx) {
if (idx >= word.length()) return false;
Node node = nodes[word.charAt(idx) - 'a'];
if (node == null) return false;
if (idx == word.length() - 1 && node.isEnd) return true;
return node.search(word, idx+1);
}
private boolean startsWith(String prefix, int idx) {
if (idx >= prefix.length()) return false;
Node node = nodes[prefix.charAt(idx) - 'a'];
if (node == null) return false;
if (idx == prefix.length() - 1) return true;
return node.startsWith(prefix, idx+1);
}
}
}